Nora Eye Care Technology
You want to know you are in the right hands if you have an eye disease that requires ongoing care such as Glaucoma, Diabetic Retinopathy, Keratoconus, Cataracts, or Macular Degeneration. All of our doctors at Nora Eye Care are trained in medical optometry, and we work closely with a network of local surgeons if further treatment is required. Your optometrist will determine the best care for your eyes, using our cutting edge medical devices to help monitor your disease.
Our office is equipped with:
Humphrey Visual Field Analyser and Virtual Field
The Humphrey Visual Field Analyser and the Virtual Field test for peripheral vision loss.
Humphrey field analyser (HFA) is a tool for measuring the human visual field that is commonly used by optometrists and ophthalmologists, particularly for detecting vision loss related to glaucoma, retinal disease, nerve disorders, and brain pathology. The results of the analyzer identify the type of vision defect. Therefore, it provides information regarding the location of any disease processes or lesion(s) throughout the visual pathway. This guides and contributes to the diagnosis of the condition affecting the patient’s vision. These results are stored and used for monitoring the progression of vision loss and the patient’s condition.
Virtual Field
The Virtual Field is a new way to test for peripheral field loss using virtual reality. This headset allows for better patient comfort, quicker test duration, and accessibility while providing robust data and comparison to previous test results that is nearly equivalent to the Humphrey Field Analyser.

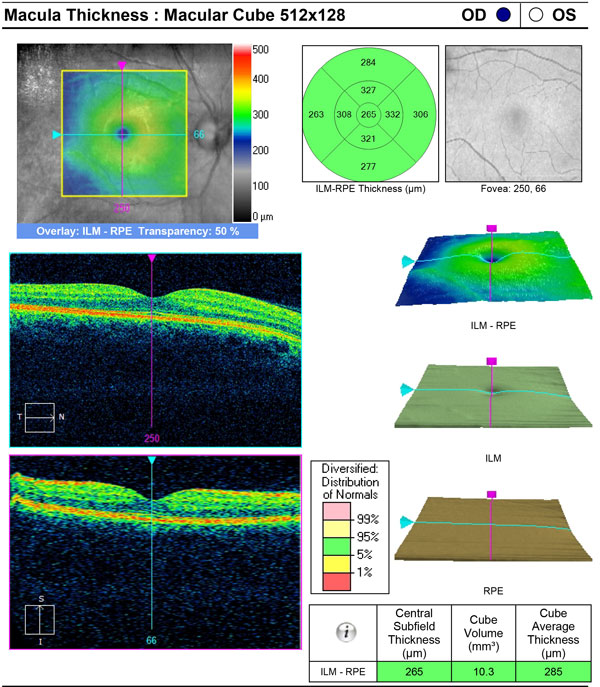
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) scanner
Optical Coherence Tomography gives a cross-sectional view of the microscopic layers within the retina and measures their thickness.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a technique for obtaining sub-surface images of translucent or opaque materials at a resolution equivalent to a low-power microscope. It is effectively “optical ultrasound”, imaging reflections from within tissue to provide cross-sectional images.
OCT has attracted interest among the medical community because it provides tissue morphology imagery at much higher resolution (less than 10 μm axially and less than 20 μm laterally) than other imaging modalities such as MRI or ultrasound.
The key benefits of OCT are:
- Live sub-surface images at near-microscopic resolution
- Instant, direct imaging of tissue morphology
- No preparation of the sample or subject, no contact
- No ionizing radiation
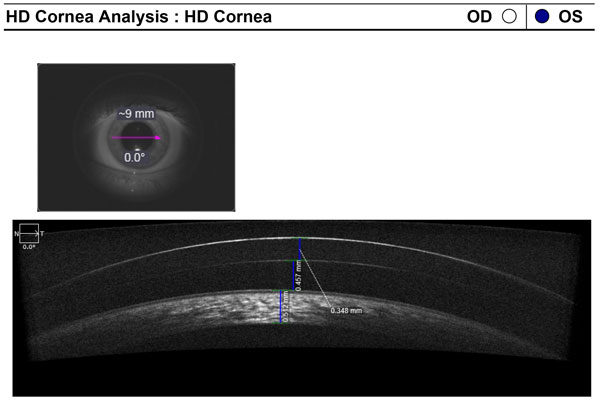
Pachymeter
A Pachymeter measures corneal thickness.
Conventional pachymeters are devices that display the thickness of the cornea, usually in micrometres, when the ultrasonic transducer touches the cornea. Newer generations of ultrasonic pachymeters work by way of Corneal Waveform (CWF). Using this technology the user can capture an ultra-high definition echogram of the cornea, somewhat like a corneal A-scan. Pachymetry using the corneal waveform process allows the user to more accurately measure the corneal thickness, verify the reliability of the measurements that were obtained, superimpose corneal waveforms to monitor changes in a patient’s cornea over time, and measure structures within the cornea such as micro bubbles created during femto-second laser flap cuts.
Autorefractor and Autokeratometer
A Autorefractor and Autokeratometer measure central corneal curvature and estimates the patient’s glasses prescription.
An autorefractor or automated refractor is a computer-controlled machine used during an eye examination to provide an objective measurement of a person’s refractive error and prescription for glasses or contact lenses. This is achieved by measuring how light is changed as it enters a person’s eye.
Meibography and MiBo ThermoFlo
Meibography
Meibography is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses infrared light to examine and photograph the meibomian glands. Nestled in the upper and lower eyelids, the meibomian glands produce the oily part of the tears. This oil, or meibum, provides a protective outer layer of the tear film and prevents the aqueous part of the tears from evaporating quickly. In the most common form of Dry Eye Syndrome, the meibomian glands become stagnant, blocked, or atrophied. Meibography allows optometrists to determine the extent of the drye eye and guide treatment options.
MiBo ThermoFlo
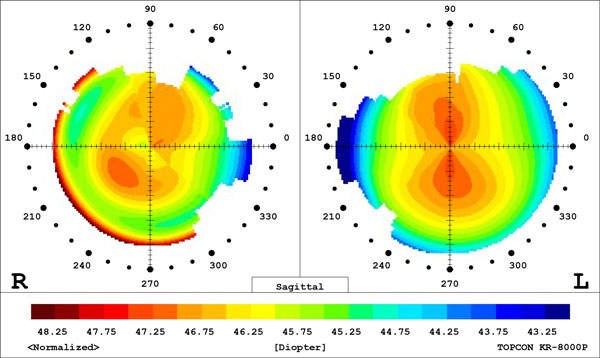
Corneal Topography
Corneal topography is a special photography technique that maps the surface of the clear, front window of the eye (the cornea). It works much like a 3D (three-dimensional) map of the world, that helps identify features like mountains and valleys. But with a topography scan, a doctor can find distortions in the curvature of the cornea, which is normally smooth. It also helps doctors monitor eye disease and plan for surgery.
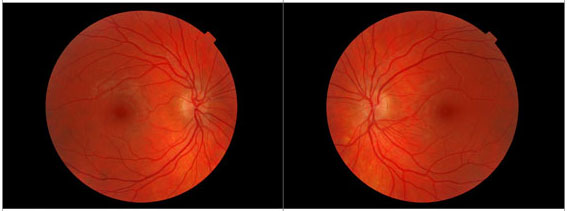
Fundus Photography
With fundus photography, a special fundus camera points through the pupil to the back of the eye and takes pictures. These pictures help your eye doctor to find, watch and treat disease.
Fundoscopy, especially when the pupils are dilated for a more complete view of the entire retina, allows for examination of the retina to help diagnose conditions and identify risk factors for potential vision loss associated with the retina. For example, patients with diabetes should have an annual dilated fundus examination to check the retina for signs of diabetic retinopathy that could lead to permanent or difficult-to-treat vision loss. Signs of diabetic retinopathy, which is often a sign also of systemic disease associated with diabetes, include bleeding, inflammation, lack of oxygen, and other problems with the retina that can lead to permanent vision loss. Fundoscopy can also help diagnose other diseases such as infection or inflammation in the eye that requires treatment to preserve vision.